Thinking logically
Structured approach keeps programs and code readable, hence easier to update. Using statements like if/else, loops and sequences. Languages like python and JavaScript are block-structured languages, using the structured approach. Some tools for designing algorithms include
- flow diagrams
- pseudocode
- maybe even logic gates
To test your algorithm you could use a trace table
Thinking concurrently
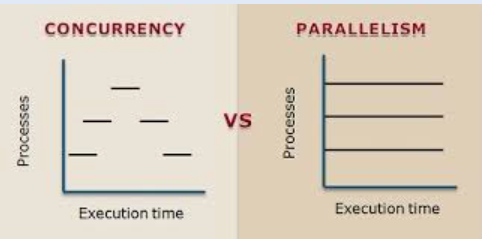
Parallel computing needs multiple different processors working parallelly (at the same time). Concurrent processing is when multiple processes are happening and each gets some focus from the single processor.
Problem recognition
There are different ways to solve problems:
- enumeration
- simulation
- theoretical approach
- creative solution
1. Enumeration
Solving problems exhaustively since computers are very fast. However even if fast it can still take time to solve everything so this is inefficient for bigger problems.
2. Simulation
It is designing a model to be used for real issues, in order to understand them. This has many important uses, e.g climate change, population predictions or design problems. It’s often used with abstraction see my other page. Simulation could be coded, used in maths, or even built in reality. Like planes or ships. It is useful when testing the real thing isn’t a viable option.
3. And 4. Aren’t worth mentioning (??)
Some strategies for problem solving is to:
divide and conquer, reducing the size of the problem with each iteration
or problem abstraction where you remove details until the problem becomes a solution
Or Automation where the computer can analyse the data from your model for you.
Problem solving
Visualization is important to understand the problem. A computer may understand binary, compromise on a table but humans get graphical or ‘pretty’ visualisations. A flow chart is good for this.
Backtracking is methodically trying out sequences until you have a solution. Usually for solving mazes, when you forget the left hand rule.
Data mining is going through ‘big data’ (a massive set of data) and finding hidden connections that are interesting, boring or a solution.
Heuristic methods are getting an approximate answer to intractable problems that usually take too long by brute force. It trades accuracy for speed, e.g when I code something that ‘works’ but isn’t efficient.
Performance modelling is using maths to test a network under conditions that are difficult to test naturally
Pipeling is splitting work up, to run like an assembly line